What is Mongoose?
According to Mongoose, Mongoose is an elegant MongoDB object modeling for Node.js. It provides a straight-forward, schema-based solution to model your application data.
Basically, Mongoose is a package which helps us interact with Mongo DB. It is a JavaScript layer on top of Mongo DB, and it adds some extra special methods that makes our live easier.
How to Install Mongoose?
The installation is very simple. We just need to npm install mongoose in our server. Then, we create a JavaScript file, and require the mongoose.
Since the Mongoose needs to interact with MongoDB, we need to open another terminal window to call "./mongod"and make sure the MongoDB is running .
Then, we connect Mongoose with MongoDB: mongoose.connect("mongodb://localhost/score_app").
Score Database Project Study
In this project, I am going to create a score app which contains student score data. The score data includes three main entries: name, gpa, and subject.
- Adding New Score to the Database
Once we connect the Mongoose with MongoDB, we need to define "scoreSchema" by creating a variable. It tells the JavaScript that we want to be able to add score to our database. A score should be define like this:
We compile the scoreSchema into a model which is "new mongoose.Schema()". And we save it to a variable score. In this model, it takes that score pattern and builds this complex model that has all of the method we need to use.
Now we can start to use that score variable to create some new scores. The first score data I create is for student name "Zark" whose Math GPA is 3.3.
Even we add the new data, it is not saved to our database yet. We need to use name.save() method to save it to our database. We pass a call back function to save, and this function will be called when save is done.
In the call back function, we give two parameters. The first one is to check if there has any potential error such as internet connect fail or code is not correctly. The second one is the score we want to return.
When I run the score.js, it shows the data I just created, and it is saved to database successfully.
Then, I added a new score data by using the same method, and it is also saved to database.
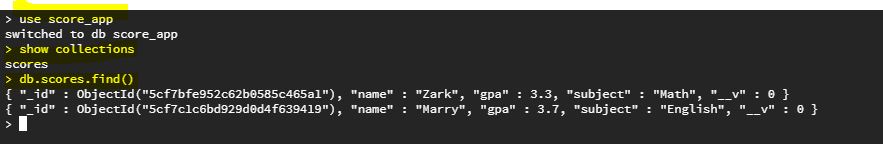
If we want to view all the data, we can run MongoDB by type "mongo", and type use "score_app), then find our scores.
- Retrieving Scores From the Database
If we want to retrieve our score data from the Database, we need to use find method: Score.find({}, function(){}).
We are passing an empty object in the find method because we are not looking for a particular score. The function also has two parameters: one is to check error, and one is scores which is the result of our find.
At the end, we run the score.js, and it retrieves all the scores data from database.








Comments
Post a Comment