What is Git?
According to Git website, Git is a free and open source distributed version control system designed to handle everything from small to very large projects with speed and efficiency. Basically, we can use Git to track all of changes and revert them back if we made mistakes.The version control system is a way for us to work with different versions of our code, so that we can save different features and make notes as we progress. It is also very useful for team collaboration.
Six Git Command You Should Know
1. Git Init
In our server, we need to create a "Git" directory and inside of "Git", we make another direcory "git_inro". Then, we add a file "app,js" in the "git_intro" folder.The first thing we need to run is "git init". When we run git init, it will make a directory which is hidden called ".git". Wherever I run that git init command, it's going to track all of our changes.
2. Git Status
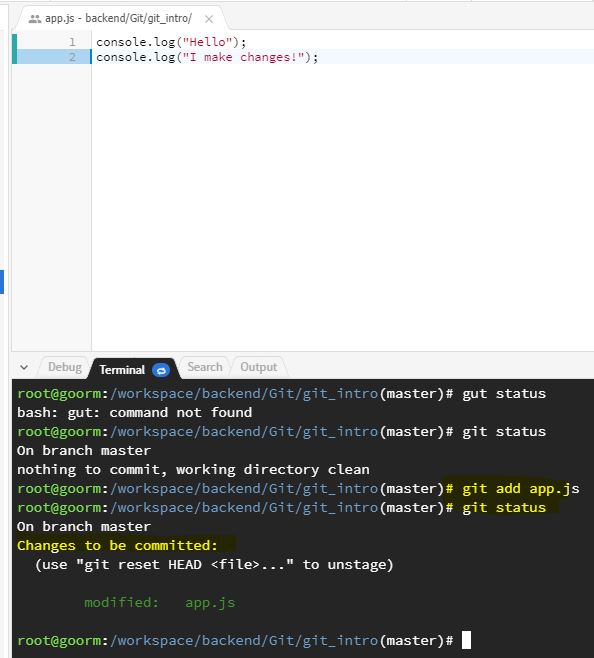
Git status asks for a status which is a common process to run before we do anything else. It shows untracked file "app.js". The reason that it is untracked because by just initializing a repository in a folder, it doesn't automatically track every file and every change.
If we don't want Git to track some files, we can tell git to ignore.
3. Git Add
Git add allows us to add the files and tell the git those are the files we want to track.4. Git Commit
Git add and git commit are the two step workflows to make the track process work.
Then, we commit which is is basically making a check point in time with changes that you have added.
The "-m" is short for "-message". It allows us to type in a commit message to describe what the what the things we are saving.
Then, we git add app.js to track the file, and check the status. It shows that changes to be committed. This means that the new file is what is going to be saved.
5. Git Log
If we want to go back to the old version. The first thing we want to do is run "git log". It will give us a history of all the commits that we have made.
Once we enter, we can see the author name, email, date, and commit message. The most important thing is the long commit string which on the top of author. This commit string is the unique identifier. We will use this number to checkout the file.
6. Git Checkout
We copy the long number and paste after "git checkout", what we will receive is a message about warning us that we should probably add and commit or get rid of it entirely. The "detached Head" is basically a pointer in space or in time.
Usually we use check out to just go look some old changes, to check out old code and then go back to where we were.






Comments
Post a Comment